
-
Architects: Alsar Atelier, César Salomón, Oscar Zamora, Yazmin Crespo
- Area: 24 m²
- Year: 2024
-
Photographs:Mateo Pérez

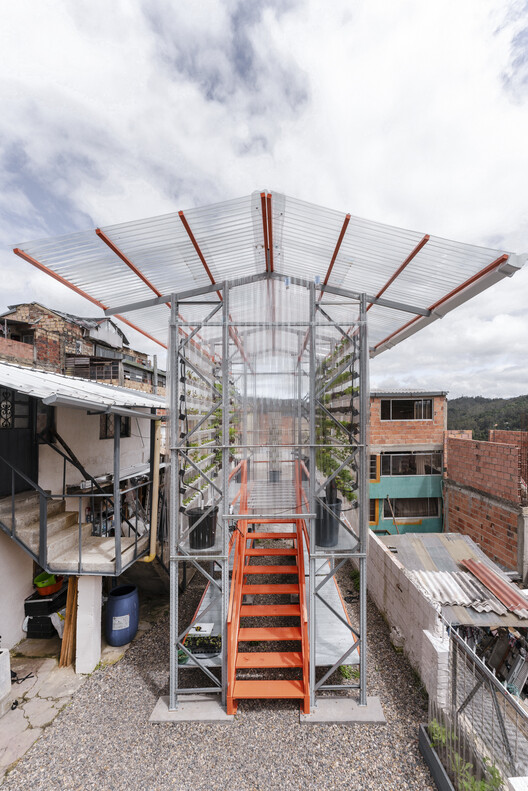
Text description provided by the architects. The project supports initiatives led by community leaders and local organizations, such as Cesar Salomón, Fondacio Altos del Cabo, and Maya Tejedores de la Tierra, who have been cooperating, collaborating, and participating for seven years in the informal neighborhood of San Luis in Bogotá. These collaborations have impacted hundreds of residents and have supported the hydroponic agriculture initiative as an alternative for healthy nutrition in Bogotá’s self-built contexts, where the most prevalent diseases tend to be obesity and diabetes.

On the other hand, hydroponics is a cultivation system in which plants grow in an inert substrate or directly in a nutrient solution in water, allowing crops to be arranged on a vertical axis. This system offers a plant density 2 to 10 times higher, up to 60% water savings, healthier food, and the ability to grow crops in any climate or season. Given the high density in self-built contexts, hydroponics becomes an excellent alternative to traditional agriculture, which requires large land areas.


The architectural design of the module, designed by Alsar-Atelier + Oscar Zamora and funded by the NEACOL organization, emerged from the repurposing of an industrial shelving system—originally a consumerist material—into a solution that enables social construction: fast and reusable. The physical formation of informal cities is often variable and temporary due to issues of occupation and legality. However, the primary construction materials remain concrete and brick, which are inherently permanent.
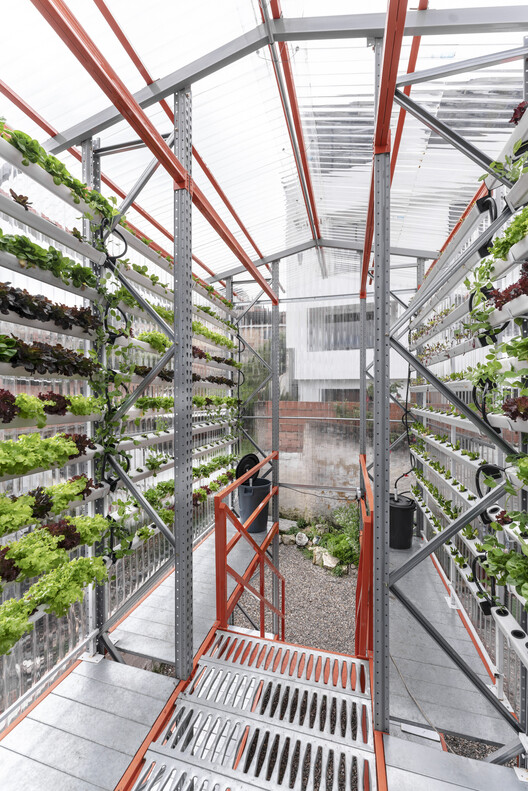
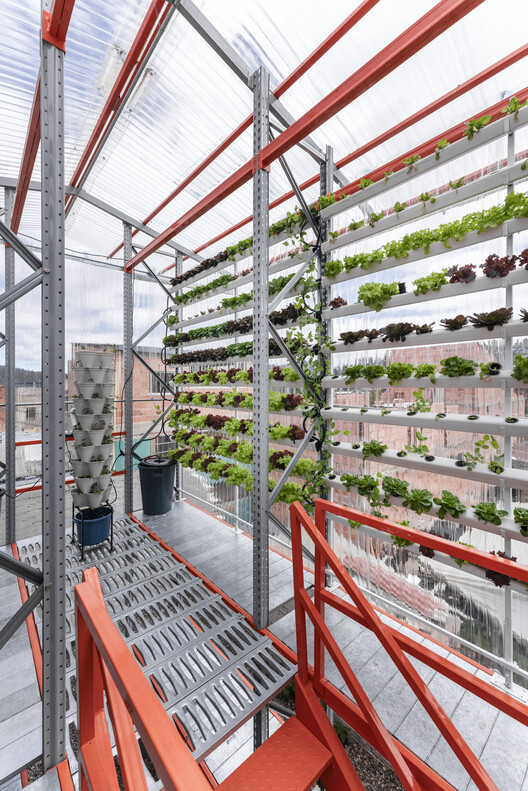




Therefore, the module is designed as a lightweight and semi-permanent structure to integrate into this territorial reality. Additionally, the project is designed with the foresight of being dismantled if needed, allowing its components to return to their original use without generating waste or being relocated to another vacant lot, where the modular design can expand or shrink accordingly.

Beyond serving as a hydroponic module—adapting industrial shelving for easy transport, assembly/disassembly, and reuse, while reducing construction time to one week—the project functions as an analog school that will support the Altos del Cabo Center by training the community in hydroponic farming through new workshops.


Additionally, it will provide space for personal on-site cultivation, sustainable water use, and collective post-harvest activities, fostering inclusion and self-management. The design integrates with urban gardening workshops and houses the eighth Seed Bank of Chapinero from the José Celestino Mutis Botanical Garden, preserving 43 native and heirloom species. In conclusion, the project is an excellent example of tactical, sustainable, and low-cost architecture addressing the challenges of self-built environments in Colombia.



















